- 01 Introduction
- 02 Biology of DNA
- 03 Practical Issues Specific to DNA Evidence
- 04 Introduction to the Forensic DNA Laboratory
- 05 Assuring Quality in DNA Testing
- 06 Understanding a Forensic DNA Lab Report
- 07 Statistics and Population Genetics
- 08 Mitochondrial DNA & Y-STR Analysis
- 09 Forensic DNA Databases
- 10 Collection of DNA Evidence from Suspects and Arrestees
- 11 Pretrial DNA Evidence Issues
- 12 Victim Issues
- 13 Trial Presentation
- 14 Postconviction DNA Cases
- 15 Emerging Trends
Principles of Forensic DNA
for Officers of the Court
for Officers of the Court
Module 8 :: mtDNA & Y-STR
Topic 3 :: mtDNA Considerations
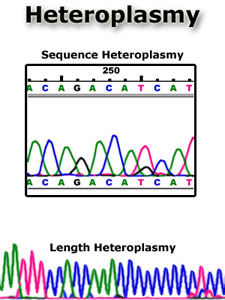
Heteroplasmy
Heteroplasmy is defined as the presence of more than one mtDNA type within a single individual. Heteroplasmy was originally believed to be rare among healthy individuals, but scientists now believe that each person has some low- frequency, slightly different mtDNA types mixed in with his or her inherited dominant type. These low-frequency types arise from mtDNA mutations within growing and dividing cells. The two types of heteroplasmy are length heteroplasmy and sequence (or site) heteroplasmy.
